Risk Management at State DOTs: Building Momentum and Sustaining the Practice (2025)
Chapter: Key Findings
Key Findings
Through the research conducted, the research team determined several key conclusions. It reviewed the findings from the literature review and gap assessment, industry roundtable, case studies, and state DOT focus group, and the key findings under the four overarching categories are as follows.
Culture of Risk and Organizational Change
Creating a culture of informed risk-taking within an agency enables and rewards individuals and groups for taking the right risks in an informed manner. Agencies that have found the greatest success in building and sustaining risk management have highlighted the value of establishing a supportive internal culture. Staff at every level of the organization must shift mindsets from siloed to cooperative approaches, including updates to organizational structure, staff education, and cross-discipline representation. Although such cultural shifts happen within the broad body of an agency’s staff, they must be initiated by agency leadership starting from the top down.
Process Improvement
To support the operational changes that come along with integrating management practices, agency policy, and subsequently organizational structure, also may have to change. Steps in this change include reconfiguring business processes, realigning agency objectives, or institutionalizing new key practices. This will look different for each agency depending on its unique context and needs, although it may occur in a few common ways.
Communication and Promotion
Buy-in from leadership and at an executive level is essential to building and sustaining risk management within an agency, which ultimately enables informed risk-taking. Support from leadership is the most common starting point among successful agencies. Educating staff on the everyday risks its agency may face is important to aid in mitigating them. It is also important to educate staff on the benefits of mitigating certain risks to understand why risk management should be integrated.
Data, Tools, and Risk Quantification
Providing guidance documents, examples, and tools is key to helping agencies build and sustain risk management.
Digital Content and Website
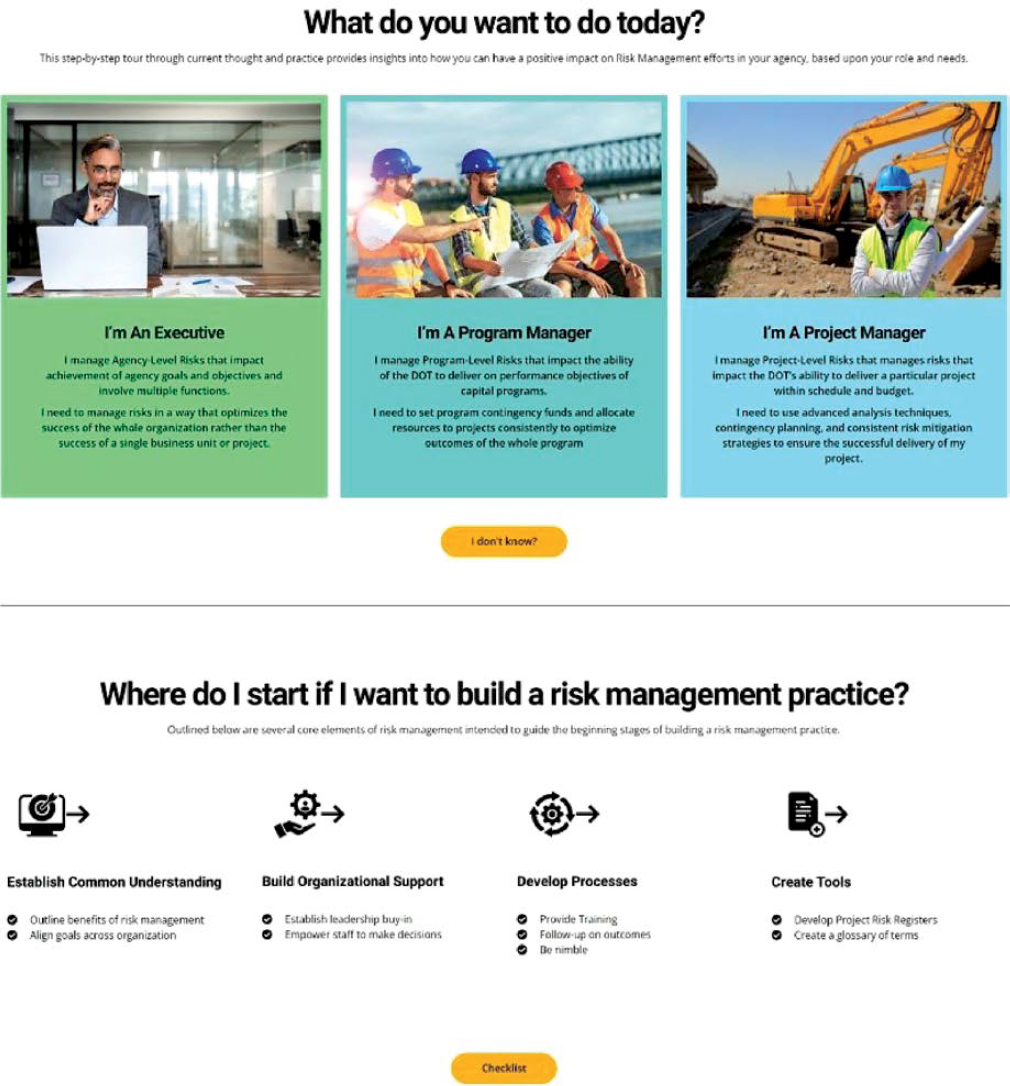
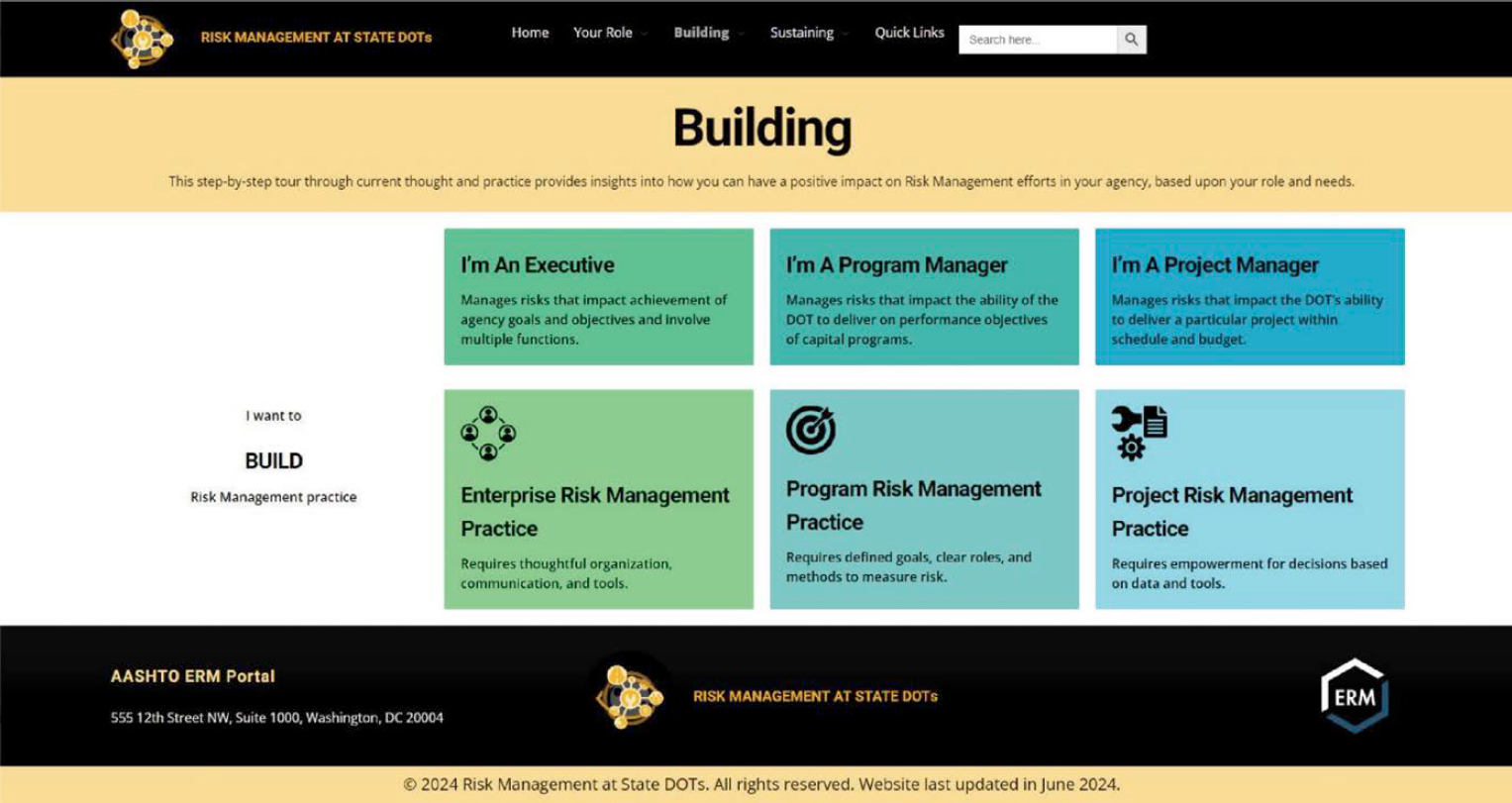
Based on the results of the research and feedback from the project panel and other state DOT practitioners, the content for the website covers the key elements described previously. The website is an easy-to-navigate platform for practitioners at different levels of an agency and in different places on a risk management spectrum. The website can be accessed on the AASHTO Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Portal (https://www.erm-portal.com/tool-library/). Figures 5 and 6 provide screenshots of the design of the website home page and a content page, respectively.