A Review of the Landscape Conservation Cooperatives (2016)
Chapter: Appendix C: Guidance for Landscape Conservation Planning and Designs
Appendix C
Guidance for Landscape Conservation Planning and Designs
LESSONS LEARNED IN DEVELOPMENT OF LANDSCAPE CONSERVATION PLANS
It will be helpful for Landscape Conservation Cooperative (LCC) planners and practitioners to be aware of some of the most important lessons learned and best practices in conservation planning (Groves and Game, 2015):
- Multiple objectives. Early conservation plans were traditionally focused on a singular objective—conserving biodiversity (e.g., Groves et al., 2002). Today, most landscape conservation planning efforts will be trying to achieve multiple objectives, particularly those of the LCCs where so many different stakeholders and interests are engaged. Some of these objectives will be oriented toward biological features of the landscapes (targets), while other may be directed at cultural resources or ecosystem services. There are sophisticated planning tools for evaluating, comparing, and in some cases, conducting trade-off analyses between what may be competing objectives (e.g., Moffett and Sarkar 2006). There are now many examples of multiobjective planning within the conservation planning field. Marine spatial planning is one of the better known examples of planning for multiple objectives (Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission, 2009).
- All forms of science. Although traditional conservation plans focused primarily on the disciplines of ecology, wildlife biology, and conservation biology, many planners now appreciate that the disciplines of economics, social science, and political science will also make major contributions to landscape conservation plans. This situation is most easily recognized at the beginning of a planning effort when a team does a “situation analysis” that places the planning effort within the context in which it will occur and is increasingly referred to as the socio-ecological system—an acknowledgment that in most if not all landscapes the social, economic, and ecological systems are really one integrated system in which planning must be conducted (Ban et al., 2013).
- Integration of spatial and strategic planning. Conservation planning was designed to answer two basic questions: Where should conservation take place on the ground (spatial planning) and how should it be achieved (strategic planning; Redford et al., 2003)? The two types of planning—spatial and strategic—are often conducted in separate processes that are poorly integrated. Spatial planning—or the location of areas important for biodiversity conservation—has dominated the field and we see evidence of that in the initial efforts in LCCs (i.e., the conservation blueprint-type maps). The most effective conservation plans are likely to be those that closely link the identification of places important for conservation with the strategies and actions necessary to achieve conservation (Game et al., 2013). Places for achieving conservation in and of themselves are not priorities; it is the actions that we need to take to conserve these areas that need to be prioritized because the actions take resources and we get various levels of return on investment for those actions and resources spent. The take-home message is that LCC landscape plans should spend just as much effort evaluating what types of strategies and actions to implement as identifying the areas for taking those actions.
- Evidence-based approach. Thousands of conservation strategies and actions are being implemented every day—some succeed and some fail. At least two components of conservation planning can help in determining and implementing conservation strategies and actions that are more likely to succeed. The first of these is using a theory of change (see Figure C.1; CMP, 2013), in which the succeeding steps of a conservation strategy are diagrammatically represented so that the underlying logic of how the strategy is likely to succeed is examined through a series of steps in which each intermediate result from an action is portrayed in the results chain. The second is taking an evidence-based approach to selecting and implementing strategies and actions. In short, this means providing the evidence from experience or scientific literature that a particular conservation action is likely to succeed (Cook et al., 2010). For example, if a landscape
- Using risk analysis. Risks are simply uncertain events that could have a negative impact on the outcome of a conservation project. Certainly one of the underlying reasons for the creation of LCCs was the risk that climate change impacts could pose on the natural heritage of the United States. Yet, despite the fact that most scientists, planners, and practitioners know that there are various types of risk involved in conservation planning and implementation, few plans consider risk to any significant degree. The good news is that there are tried-and-true methods that can be integrated into conservation plans that will enable LCCs and others to better evaluate risks, and to ultimately implement strategies and actions in places that are more likely to succeed (Burgman, 2005).
- Planning-to-implementation gap. A great deal has been written about the gap between developing a landscape conservation plan and implementing it (e.g., Knight et al., 2008). Because it remains unclear in these early years of the LCC Network whether the LCCs themselves are or can be an implementing body, any landscape conservation planning efforts need to pay particular attention to who the target audiences are for a conservation plan, and who will implement it, especially for strategies and actions that need to take place over multiple geopolitical jurisdictions. Here are a few tips to be on the lookout for to avoid some of pitfalls of poor implementation:
suggests that a dam needs to be operated in a different fashion to provide more water downstream at particular times of year for endangered mussels, then there needs to be evidence evaluated and provided that such an action is likely to succeed.
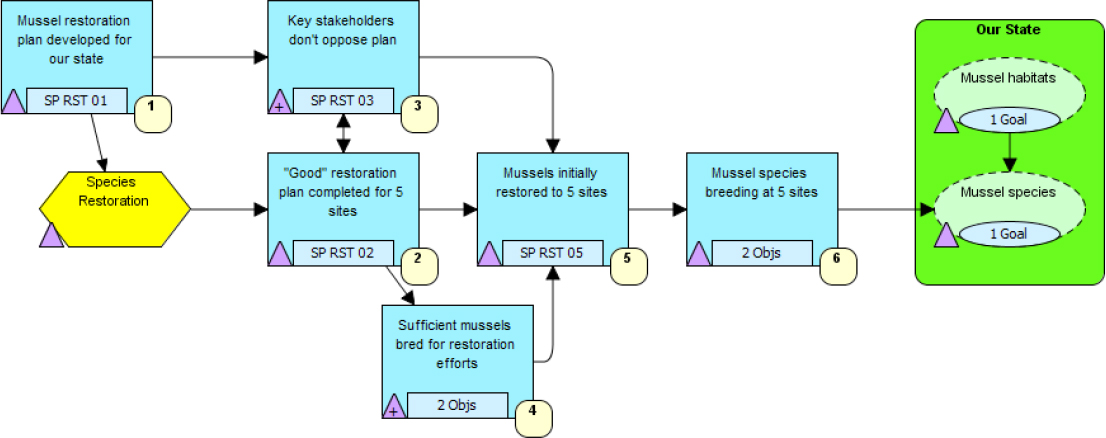
SOURCE: Used with permission from Conservation Measures Partnership (http://www.conservationmeasures.org).
- Many plans are simply too long and too detailed for stakeholders to understand. Shorter and succinct is better.
- Too few plans give enough consideration to the financial and staff costs of implementing them. Money matters.
- Some planning efforts lack engagement from those who will be charged with implementing them. It is an age-old adage but a person is more likely to be involved in solving the problem if he or she helps come up with the solution.
- Some plans fail to articulate the conservation problem they are intended to address. Another way of thinking about this is that plans need specific objectives around which a set of prioritized conservation actions can be developed. “Prioritized” is the key word in this phrase; too many plans have long laundry lists of strategies and actions that lack a sense of priority and reality in the resources available to act on them. Plans that are more likely to succeed will spend considerable effort on developing a short list of high-priority strategies and actions and determining who will be responsible for them.
ILLUSTRATIVE COMPONENTS OF A REGIONAL CONSERVATION PLAN OR LANDSCAPE CONSERVATION DESIGN
Although all landscape conservation plans will take different forms depending on the desires of the stakeholders and the planning team, in one form or another the components
outlined below should be part of the documentation process of any landscape planning effort. Different audiences will need varying levels of information about these components. How the plan is communicated will be a critical aspect of its success. Above all else, it is helpful to keep in mind why landscape conservation planning and design are so important: it is to help ensure that conservation practitioners are making informed decisions on the strategies and actions that will help them achieve their ultimate conservation goals and objectives.
- The Executive Summary is perhaps the most important section of the plan because many readers will not get beyond it; it’s also a useful section for fundraising and outreach.
- Planning context includes the purpose of the plan, decisions to be made, decision makers, audience, constraints, or sideboards from previous planning efforts or law and policy.
- Planning team and process includes members, skill sets, organizations involved, team charter, management process, and roles.
- Situation analysis involves the economic, social, ecological, and political trends and opportunities within the socio-ecological system; it usually includes a conceptual model and assessment of threats to conservation features and may also include some analysis of enabling conditions for conservation and likely barriers to implementation.
- Project scope is the strategic, geographic, and temporal “boundaries” of the project.
- Fundamental objectives and desired outcomes include the ultimate outcomes in a conservation project that one hopes to achieve—the ends not the means—and those things that one cares most about.
- Conservation features are the elements of biodiversity, ecosystem processes, and social (human well-being) elements that are the focus of the planning efforts and, where appropriate, the quantitative targets (or goals) that have been set for these features.
- The range of strategies are the different strategies or major interventions that are under consideration for use in a conservation project or program and a rationale for how decisions will be made to focus on certain strategies and not others.
- Strategy selection and theory of change involve the strategies that a project or program has selected to implement and a rationale for how and why those strategies will be implemented.
- Data and knowledge are a summary of the types of data, knowledge (expert, local, traditional), and associated metadata that are used in the plan.
- Risks are those factors considered most likely to influence the successful implementation of strategies.
- Monitoring program is a plan for what actions will be taken during the project to measure progress and evaluate the effectiveness of strategies and actions.
- Work planning involves a detailed timeline of actions and tasks required to implement the plan, who is responsible, and proposed deadlines.
- Budgeting and fundraising involve detailed assessment of the staff and financial resources needed to implement the strategies and actions and a realistic fundraising plan to ensure that these resources are in place.
- Communication involves a summary of the different types of internal and external communications that will take place related to the project (e.g., websites, press releases, blogs, and field trips).
- Operational or implementation plan provides details on how the plan will be implemented.
COMMITTEE ANALYSIS
The illustrative components of a Landscape Conservation Design listed above will be critical components for the LCCs to include when developing their Landscape Conservation Designs. As discussed in great detail in Chapter 4 and to some extent in Chapter 6, developing metrics and approaches to account for on-the-ground conservation actions will be important, yet difficult for the LCCs. In contrast to the Joint Ventures, LCCs do not have the authority to deliver conservation actions. However, the LCCs can demonstrate how they contribute to on-the-ground conservation by developing—as part of the Landscape Conservation Design—a good theory of change, a monitoring program, and a clear work plan (see components, above).
This page intentionally left blank.



